|
Contents
1. Corporate Venture Strategies
Achieving Top-line Growth and
Bottom-line Results
Distinctive Features of Radical
Innovation Projects
Radical Innovation vs. Incremental
Innovation
Internal and External Ventures
Success Story:
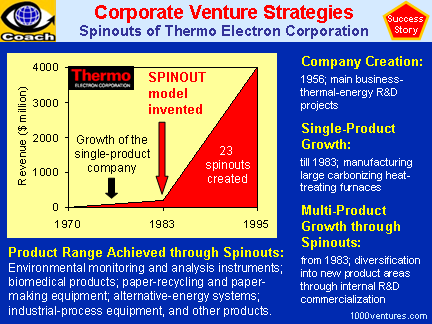
Spinouts of Thermo Electron Corporation
Success
Story: In-company Ventures by Corning
Success
Story:
Corporate Venture Investing by GE Equity
Entrepreneurial Strategies and Skills
5 Critical Success Factors for New
Ventures
2. New-to-the-World Product Development
Product Innovation: New Product Types
Success
Stories:
Challenging the Status Quo
Engaging Cross-functional Teams
Loose-Tight Leadership
12 Recommendations for Stimulating
Radical Idea Generation
Make Decisions Quickly
Techniques for Fast Evaluation of
Innovative Ideas
Innovation Football Simulation Game:
Evaluating the Idea and the Team
Experimentation the Key to Discovery
Keys to Successful Market Learning
A Different Role of Prototyping
Keeping Eyes Open for Inspiration
DOs and DON'Ts of a Successful
Innovator
High-Growth Business Development
Roadmap
3.
Creating a Winning Business Model
Business Model: Connecting Internal
Inputs to Economic Outputs
7 Elements of a Business Model
See
the slide
Success
Story:
Amazon.com Creating Value and Competitive Advantage
The Tao of Customer Value Creation
Market Development Trend
Brand Building and Product Marketing
Success
Story:
Half.com Innovative Buzz Marketing
Extended Enterprise
Core Competencies
Customer Partnership
Strategic Alliances
Innovative Revenue Models
Competitive Strategies
See
the slide
Differentiation Strategy: Three Parts
and Four Steps
Weak and Strong Differentiation
Strategies
4 Types of Marketing Warfare
Barriers to Market Entry
Sustainable Competitive Advantage: 5
Criteria
Sustainable Competitive Advantage:
Synergy of Capabilities
See
the slide
4. Managing a Radical Innovation Project
Managing Innovation vs. Managing
Operation
Radically New Product Development: Key
Uncertainties and Discontinuities
Fuzzy Front End
Radical Innovation
Specific Skills of Radical Project
Managers
Corporate Innovation System
Strategic Intent
Tips for Making the Vision a Reality
Creating a Relentless Growth Attitude
Innovation Process: Traditional vs.
Flexible Model
Project Administration vs. Business
Synergies Approach
Managing Innovation Projects: Business
Synergies Approach
Leading Systemic Innovation: Empowering
Cross-functional Teams
Best
Practices: Cross-functional Innovation Teams at
Quantum
Top-Line Success = Creative Chaos x
Productive Structure
See
the slide
Best
Practices: Attributes of Effective Innovation in
Silicon Valley
Best
Practices: Measuring Innovation by Silicon Valley
Companies
Best
Practices:
Predictive Innovation Measures Used in Silicon Valley
Fast Company
Launching a Crusade
Establishing Corporate Guiding
Principles
Owning Your Competitive Advantage
Strategies for Building a Growth
Culture
Best
Practices:
Structure of Silicon Valley Firms
5. Entrepreneurial Leadership
Corporate Management vs. Venture
Management
Building Attributes and Delivering
Results
Entrepreneurial Leader: Ten Key Action
Roles
Talent, Temperament and Technique
Synergy
Lessons
from Jack Welch: 4Es of Leadership
Specific Attributes of Entrepreneurial
Leaders
See
the slide
Inspire Your Team
Lessons
from Silicon Valley Firms: Getting the Most from
Knowledge Workers
Making Big Changes: 10 Questions To
Answer
10 Extreme Leadership Best Practices
Strategic Achievement
80/20 Strategic Thinking
Turning Failures into Opportunities
Inspiring People
See
the slide
Energizing People
Freedom to Fail
Lessons
from Silicon Valley Firms: The Fun Factor
Best
Practices: Silicon Valley Companies Sharing Gain
With Employees
Best
Practices: Pre-IPO Company Ownership
6. Psychology of
Achievement
Great Achiever: 8 Winning Habits
Yin-Yang of Achievement
Yin-Yang of Influencing People
Achievement-focused Self-Coaching
4 Powerful Attitudes
Take Risk
Never Give Up
7.
Entrepreneurial Creativity
Entrepreneurial Creativity: 4
Intertwined Pillars
The Tao of Value Innovation
See
the slide
Be Different and Make a Difference!
See
the slide
Challenging Assumptions
Thinking
Outside the Box
Idea Evaluation: 4Χ2 Perceptual
Positions
5 Steps to Entrepreneurial Creativity |
Sample Ten3 SMART Lessons
(Slide + Executive Summary)

Two Components of
Sustainable Growth Strategy
Sustainable business growth
strategy is a practical approach to achieving top-line growth
and bottom-line results. The two main sources of sustainable
competitive advantage are:
-
Continuous Improvement
Culture: continuous effort to improve organizational
climate and productivity of the core business in response to
continuous changes in the marketplace.
-
Durable Corporate Venture
Strategy: internal investment in innovation and new
product/service development, new business creation, and
external venture investing in new technologies and emerging
markets.
Improvement
Strategies versus Venture Strategies
-
Improving Processes:
Addressing the ever-changing needs of current customers and
keeping cash flow healthy. Cost-cutting efforts can build
your bottom line.
-
Radical Innovation:
It is radical innovation and new game changing breakthroughs
that will launch your company into new markets, make you a
market leader, enable rapid growth, and create high return
on investment.
Continuous Change
as a Norm
Companies, like any living
organism, must become learning organizations that change and
adapt to suit their changing environment. If you don't practice
the change management that looks after the future, the future
will not look after you, says Bill Gates. "The tendency for
successful companies to fail to innovate is just that: a
tendency. If you're too focused on your current business, it's
hard to look ahead.
Two Types of
Change in the Marketplace
1. Organic, or continuous, change
2. Radical, or discontinuous, change driven by radical
innovation
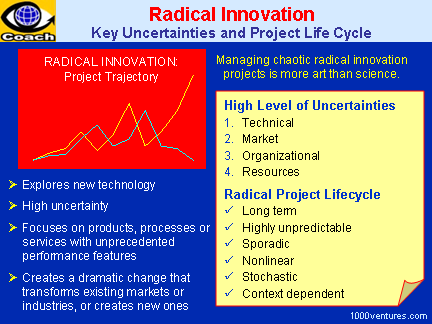
What is Radical
Innovation?
Long-term corporate success linked
to the ability to innovate. Although corporate investment in
improvements to existing products and processes does bring
growth, it is new game changing breakthroughs that will launch
company into new markets, enable rapid growth, and create high
return on investment.
Radical innovation, concerned with
exploration of new technology, is fundamentally different from
incremental innovation that is concerned with exploitation of
existing technology. Radical innovation is a product, process,
or service with either unprecedented performance features or
familiar features that offer potential for significant
improvements in performance and cost. It creates such a dramatic
change in processes, products, or services that they transform
existing markets or industries, or create new ones.
Fuzzy Front End
The early stage of the radical
innovation process is ripe with opportunity, but it is also
devoid of many definitive facts. Due to its high degree of
ambiguity, this development phase has become known as "the fuzzy
front end."
New Management
Approaches
New competencies are required to
address the challenge of radical innovation project management.
High levels of uncertainties - technical, market,
organizational, and resources - create extraordinary challenges
for project management. The problem of multiple dimensions of
uncertainty is complicated by the fact that the uncertainties
interact with one another. For radical projects to mature,
uncertainty must be reduced on all four dimensions. At the same
time, if you try to eliminate all uncertainty and control every
risk, you'll find yourself frozen in place, never doing anything
new. (Christopher Meyer)
There is practical value in
understanding the patterns in and the differences between
evolutionary incremental innovation projects and revolutionary
radical innovation projects. This understanding can help you
apply right management practices to different types of
innovation projects and make the course of radical innovation
shorter, less sporadic, less expensive, and less uncertain.
...
and much more! |