|
Contents
1.
Smart
Leader
1.1.
Character and People
Skills
Character and Personality of Highly
Effective People
The Role of Your People Skills
The Tao of Influencing People
9 Principles of Effective Negotiating
Coaching Yourself
1.2.
Technology of Achievement
COCA Principle of Achievement
Be Different and Make a Difference
The Tao of Achievement
Self-Motivation
SMART Goals
Entrepreneurial Creativity: 4
Intertwined Pillars
The Tao of Entrepreneurial Creativity
Failure as a Stepping Stone to Success
Creative Problem Solving (CPS):
Reframing
1.3.
Leadership Skills
Differences Between What Managers and
Leaders Do
12 Effective Leadership Roles
Best
Practices: Welchs 4Es of Leadership
Best
Practices: 10 Lessons from Konosuke Matsushita
See
the slide
Best
Practices: Powells Leadership Principles
Leadership Attributes
See
the slide
Inspirational Leadership: 10 Roles
See
the slide
Situational Leadership
Creative Leadership
Leadership Challenge Model: 5 Exemplary
Roles
Entrepreneurial Leaders: Specific
Attributes
See
the slide
2.
Smart
COMPANY
2.1.
Balanced Business System
The Tree of Business
See
the slide
The Key Challenges To Organizational
Success
10 Rules for Building a Sustainable
Growth Business
Rapidly Changing Global Scenario
See
the slide
High-Growth Business Development: 4
Stages
Best
Practices: Sam Walton's 10 Rules
Lessons
from Narayana Murthy, Infosys: How To Build a
Great Company
Corporate Vision See
the slide
Balanced Business System
See
the slide
Innovation Strategies for Top-line and
Bottom Line Growth
The Tao of Business Success
See
the slide
Business BLISS
The
Tao of Balanced Management
Management By Consciousness
Business Model: 1+6 Components
See
the slide
The Tao of Customer Value Creation
See
the slide
Customer Intimacy
Extended Enterprise
Core Competencies
Strategic Alliances
Business Architect
See
the slide
Business Architect: Cross-functional
Expertise Requirement
Systems Thinking
Cross-functional Excellence
2.2. Winning
Organization
9 Signs of a Loosing Organization
See
the slide
Corporate Capabilities
Shift from Industrial to
Knowledge-driven Enterprise
Shared Values
Best
Practices: Disney's Inspiring Mission and Shared Values
Best
Practices: GE Values Guide
Strategies for Building a Growth Culture
Best
Practices: Building a Flexible Culture at Dell
Computers
Success
Story: Leading Organizational Transformation at GE
Building Trust
The Tao of Employee Empowerment
See
the slide
Employee Satisfaction
Effective Motivation
Attitude Motivation
The Single Key To Team Success
Building a Team Culture
Harnessing the Power of Diversity
Creating Cross-functional Teams
Fast Company
Best
Practices:
Warren Buffett Makes Quick Investment Decisions
Success
Story: Charles Schwab
Best
Practices: Charles Schwab's Corporate Guiding
Principles
Success
Story: Eliminating Bureaucracy at ABB
Fast Company: Owning Your Competitive
Advantage
Intellectual Assets: Growing Role in
the Modern Economy
Best
Practices: Knowledge Management at British Petroleum
(BP)
Best
Practices: 4 Strategies for Raising Corporate IQ at
Microsoft
The Wheel of Knowledge Management
The Tao of Intellectual
Cross-Pollination
Coaching in the Workplace: Key Benefits
3 Types of Knowledge Organizations:
Learning, Teaching, Coaching
2.3.
Synergized Business
Processes
Best
Practices: Characteristics of the Most Successful
Companies
Process Management: Shift to Cross-functional Model
Benefits of Enterprise-wide Business
Process Management (EBPM)
Process Thinking
Eight Essential Principles of EBPM
Service-Profit Chain
Continuous Improvement Firm (CIF)
Lean Production: Removal of Waste
Activities
Quality Management: 8 Rules
Aligning IT and Business
11 Traits of a True IT Leader
3.
Smart
Strategies
3.1.
Enterprise Strategies
Three Hierarchical Levels of Strategy
Creating Sustainable Profit Growth: 9
Questions To Answer
Sustainable Growth Strategies
Strategy Pyramid vs. Strategy Stretch
See
the slide
Choosing Between Strategy and
Opportunity Approach
Strategy Programming vs. Strategy
Innovation
Best
Practices: Dynamic Strategy Formulation by Silicon
Valley Companies
Business Intelligence: 3 Levels
3.2.
Competitive
Strategies
5 Strategic Competitive Questions
Competitive Strategies
See
the slide
Success Story:
7-Part Competitive Strategy of Microsoft
Sustainable Competitive Advantage: Synergy of Capabilities
See
the slide
Four Categories of Business Tactics
Four Types of Marketing Warfare
Customer Success 360
The Top 10 Laws of Marketing
Differentiation Strategies: Weak and
Strong
Strategic Brand Management
3.3.
Strategic
Achievement
Success Rates and Major Impeding
Factors
Strategic Achievement: Thinking Χ
Action Χ Learning
Lessons
from Michael Dell:
Mobilize Your People Around a Single Goal
If You Want
To Grow: 6 Advices from Richard Branson
Strategic Intent
Searching for Opportunities
Dynamic Planning
Launching a Crusade
6Ws Chart of Change Management
Change Failure: Main Reasons
Leading Change: 8 Stages
The Tao of Change Management
See
the slide
4.
Smart
Management
4.1.
New Management Model
New
vs. Traditional Management Model
Leadership-Management Synergy
See
the slide
SuperLeadership: Leading Others To Lead
Themselves
Lessons
from Michael Dell:
Managing by Wondering Around (MBWA)
Fundamental Management Changes
Engendered by Internet
The Ideal Leader
Three Common Traits of Great Corporate
Leaders
Shift from Management to Leadership
The
Tao of Managerial Leadership
Managing Knowledge Workers
Best
Practices: Getting the Most from Knowledge Workers in
Silicon Valley
Three Manager's Skill Sets:
Manager Leader Coach
4.2.
Results-based
Leadership
Effective Leader: Attributes Χ Results
Lessons
from Steve Jobs: 12 Rules for Success
See
the slide
Results-based Leadership
See
the slide
Strategic Leadership
80/20 Thinking
Organizational Fitness Profile (OFP)
Project Management: 2 Approaches
Business Synergies Approach to Project
Management
Milestone-based Thinking
Volatility Leadership: 10 Best
Practices
Entrepreneurial Leadership
Inspiring People
See
the slide
Energizing Employees
Employee Performance Management: Holistic Approach
Performance Management: Balanced
Scorecard
Best
Practices: Leadership Development at GE
4.3.
25 Lessons from Jack
Welch
Success
Story: Creating the World's Most Competitive Enterprise
See
the slide
Lessons from Jack Welch
See
the slide
Lead More,
Manage Less
Lead
Manage Less
Articulate Your Vision
Simplify
Get Less Formal
Energize Others
See
the slide
Face Reality
See Change as an Opportunity
Get Good Ideas from Everywhere
Follow up
Build a
Winning Organization
Get Rid of Bureaucracy
Eliminate Boundaries
Put Values First
See
the slide
Cultivate Leaders
Create a Learning Culture
Harness Your
People for Competitive Advantage
Involve Everyone
Make Everybody a Team Player
Stretch
See
the slide
Instill Confidence
Make Business Fun
Build the
Market-Leading Company
Be Number 1 or Number 2
Live Quality
Constantly Focus on Innovation
Live Speed
Behave Like a Small Company
GE Leadership Assessment Survey (LES): 10 Characteristics
1. Vision
2. Customer / Quality Focus
3. Integrity
4. Accountability / Commitment
5. Communication / Influence
6. Shared Ownership / Boundaryless
7. Team Builder / Empowerment
8. Knowledge / Expertise / Intellect
9. Initiative / Speed
10. Global Mind-set
5.
Smart
Innovation
5.1.
Systemic Innovation
Innovation the Key to Success and
Survival
Evolution of Innovation from Linear to Systemic
Systemic Innovation 360: 7 Areas
See
the slide
Strategy Innovation: 4 Steps
The Tao of Value Innovation
See
the slide
The Tao of Business Process Innovation
Engaging Cross-functional Teams
Leading Systemic Innovation
Business Innovation: Four Strategies
Success
Story: Bunsha Growing Business through Spinouts
5.2. Innovation
Strategies
Best
Practices: Characteristics of Most Successful
Companies
Product Innovation: Types of New
Products
Radical vs. Incremental Innovation
Best
Practices:
Stretching Innovation Portfolio by Silicon Valley Companies
Innovation vs. Operations Management
Venture Strategies: Five Areas
Success
Story: Spinouts by Thermo Electron
Venture vs. Corporate Management
Success
Story: In-company Ventures at Corning
7 Challenges in Managing Radical
Innovation
Success
Story: Venture Investing by GE Equity
Best
Practices: Qualities of Top Managers at GE Equity
Customer Partnership
Lessons
from Michael Dell: Turn Your Customers Into Teachers
5.3. Corporate
Innovation System
Innovation System
Creating a Culture for Innovation
Strategic Alignment
Best
Practices:
Creating a
Relentless Growth Attitude
Innovation-friendly Organization: 6
Components
See the
slide
How To Lead Creative People
New Product Development by
Cross-functional Teams
The Fun Factor
Innovation Process: Two Models
Best
Practices: Innovation Process Attributes in Silicon
Valley
The Jazz of Innovation
See
the slide
The Jazz of Innovation: 11 Practice
Tips
See
the slide
Leading Innovation: Loose-Tight Leadership
Techniques for Idea Evaluation
and Decision Making
6 Thinking Hats: A Tools for Analyzing
Proposals
Best
Practices:
Facilitating
Cross-pollination of Ideas
The Tao of Experimentation
Freedom To Fail
Product Innovation Metrics
Leading Innovation: Tips for Making the
Vision a Reality |
Sample Smart & Fast Lessons
Slide
+ Executive Summary
"Leadership is the art of getting someone else to do something you
want done because he wants to do it."
Dwight D.
Eisenhower
Leadership Defined
Leadership is the process of directing
the behavior of others toward the accomplishment of some common
objectives. It is influencing people to get things done willingly!
to a standard and quality above their norm to achieve a shared
stretch goal. As an element in social interaction, leadership is a
complex activity involving a process of influence; actors who are
both leaders and followers, and a range of possible outcomes the
achievement of goals, but also the commitment of individuals to such
goals, the enhancement of group cohesion and the reinforcement of
change of organizational culture.
What is Leadership? Three simple
one-line answers by Paul Taffinder
-
The easy answer: leadership is
getting people to do things they have never thought of doing, do
not believe are possible or that they do not want to do.
-
The leadership in organizations
answer: leadership is the action of committing employees to
contribute their best to the purpose of the organization.
-
The complex (and more accurate)
answer: you only know leadership by its consequences from the
fact that individuals or a group of people start to behave in a
particular way as result of the actions of someone else.
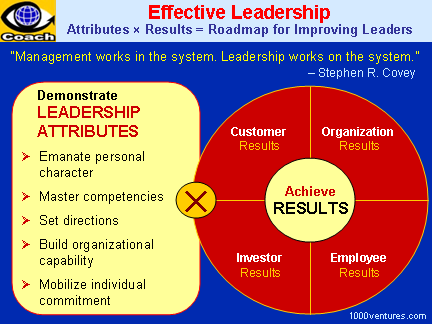
Effective Leadership
as a Source of Competitive Business Advantage
Leadership is imperative for molding a
group of people into a team, shaping them into a force that serves
as a competitive business advantage. Leaders know how to make people
function in a collaborative fashion, and how to motivate them to
excel their performance. Leaders also know how to balance the
individual team member's quest with the goal of producing synergy
an outcome that exceeds the sum of individual inputs. Leaders
require that their team members forego the quest for personal best
in concert with the team effort.
Super-leaders help each of their follower to develop into an
effective self-leader by providing them with the behavioral and
cognitive skills necessary to exercise self-leadership.
Super-leaders establish values, model, encourage, reward, and in
many other ways foster self-leadership in individuals, teams, and
wider organizational cultures.
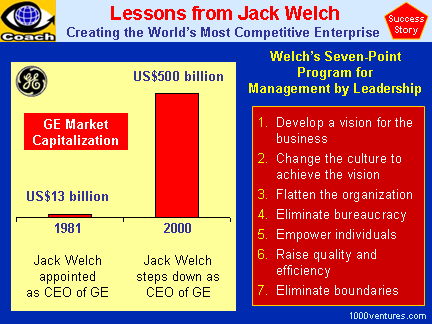
Corporate Leadership:
the Jack Welch Way
Jack Welch has been with the General
Electric Company (GE) since 1960. Having taken GE with a market
capitalization of about $13 billion, Jack Welch turned it into one
of the largest and most admired companies in the world, with a
market value of about $500 billion, when he stepped down as its CEO
20 years later, in 2000. Although Jack Welch is "the celebrated
leader of a global manufacturer often noted for its technological
prowess, he has utilized a very human process to drive change
through GE's vast organization. Having respect for the individual as
a pivotal force in organizational change, Welch created a model of
exceptional performance every corporate leader can learn from.
The Role of the
Leader in the New Economy
As Jack Welch wrote in a letter to
shareholders: "In the old culture, managers got their power from
secret knowledge: profit margins, market share, and all that... In
the new culture, the role of the leader is to express a vision, get
buy-in, and implement it. That calls for open, caring relations with
every employee, and face-to-face communication. People who can't
convincingly articulate a vision won't be successful. But those who
can will become even more open because success breeds
self-confidence."
Welch urged all GE leaders to stretch their business strategy,
"Don't ever settle for mediocrity. They key to stretch is to reach
for more than you think is possible. Don't sell yourself short by
thinking that you'll fail." Do the best possible - and then reach
beyond. Stretch "essentially means using dreams to set business
targets - with no real idea of how to get there. If you do know how
to get there - it's not a stretch target.
Employee Empowerment
Under Welch's leadership, managers had
wide latitude in building their GE units in entrepreneurial fashion.
Determined to harness the collective power of GE employees, Jack
Welch redefined also relationships between boss and subordinates. He
wrote: "The individual is the fountainhead of creativity and
innovation, and we are struggling to get all of our people to accept
the countercultural truth that often the best way to manage people
is just to get out of their way. Only by releasing the energy and
fire of our employees can we achieve the decisive, continuous
productivity advantages that will give us the freedom to compete and
win in any business anywhere on the globe."

Two Components of
Sustainable Growth Strategy
Sustainable business growth
strategy is a practical approach to achieving top-line growth
and bottom-line results. The two main sources of sustainable
competitive advantage are:
-
Continuous Improvement
Culture: continuous effort to improve organizational
climate and productivity of the core business in response to
continuous changes in the marketplace.
-
Durable Corporate Venture
Strategy: internal investment in innovation and new
product/service development, new business creation, and
external venture investing in new technologies and emerging
markets.
Improvement
Strategies versus Venture Strategies
-
Improving Processes:
Addressing the ever-changing needs of current customers and
keeping cash flow healthy. Cost-cutting efforts can build
your bottom line.
-
Radical Innovation:
It is radical innovation and new game changing breakthroughs
that will launch your company into new markets, make you a
market leader, enable rapid growth, and create high return
on investment.
Continuous Change
as a Norm
Companies, like any living
organism, must become learning organizations that change and
adapt to suit their changing environment. If you don't practice
the change management that looks after the future, the future
will not look after you, says Bill Gates. "The tendency for
successful companies to fail to innovate is just that: a
tendency. If you're too focused on your current business, it's
hard to look ahead.
Two Types of
Change in the Marketplace
1. Organic, or continuous, change
2. Radical, or discontinuous, change driven by radical
innovation

Why Business
Architect?
In today's knowledge- and
innovation-driven complex economy, business architects are in
growing demand. They are cross-functionally excellent people who can
tie several silos of business development expertise together, create
synergies, design winning business model and a balanced business
system and then lead people who will put their plans into action.
Business Architect
Defined
Business architect is a person that
initiates new business ventures or leads business innovation,
designs a winning business model, and builds a sustainable balanced
business system for a lasting success.
Business architects can be found in a multitude of business
settings: corporate change leaders, initiators of joint ventures,
managers of radical innovation projects, in-company ventures,
spin-outs, or new start-up ventures. Although the settings in which
business architects act are different, they all design and run a new
venture to achieve its sustainable growth.
Integrated Approach
to the Management Process
The integrated business systems
approach to business development and the management process is what
distinguishes modern cross-functionally excellent business
architects from functional managers. As a business architect and an
extremely effective leader, you must have a broad view to be able to
link together synergistically! the key components of corporate
success from functional planning to cross-functional cooperation,
from supply chain management to customer value creation, from the
art of continuous learning to the practice of effective
communication and influencing people and bundle them in an
intellectual, innovative and pragmatic package that can be used to
achieve sustainable competitive advantage and business growth, both
top-line and bottom-line.
Inclusive Approach
At the heart of the inclusive approach
is the belief that understanding stakeholder needs the needs of
customers, employees, suppliers, shareholders and society, and the
environment and incorporating them into enterprise strategy and
sustainable value creation activities are central to the achievement
of sustainable growth and competitiveness.
And
much
more! |