| |
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a management tool
for improving total performance.
In
TQM and
Kaizen, the cross-functional
goals of QCD (Quality, Cost,
Delivery) are clearly defined as
superior to such line functions
as planning, design, production
and sales.
|
|
 |
| |
According to the Japan
Industrial Standards,
"implementing quality control
effectively necessitates the
cooperation of all people in the
company, including top
management, managers,
supervisors, and workers in all
areas of corporate activities
such as market research and
development, product planning,
design, preparation for
production, purchasing, vendor
management, manufacturing,
inspection, sales and after-sale
services, as well as financial
control, personnel
administration, and training &
education. Quality control
carried out in this manner is
called company-wide quality
control or total quality control
(TQC)."
|
|
Mini-Kaizen
Implementing Kaizen: 7
Conditions
Deming's 14 Points for TQM
Customer-focused TQM
14 TQM Slogans at Pentel
Barriers
to successful TQM |
|
| |
Quality control in Japan deals
with quality of people. It is
the fundamental concept of the
Kaizen-style TQC. Building
quality into its people brings a
company a half-way towards
producing quality products.
|
|
Kaizen
Mindset
Japanese-style Suggestion Systems |
|

| |
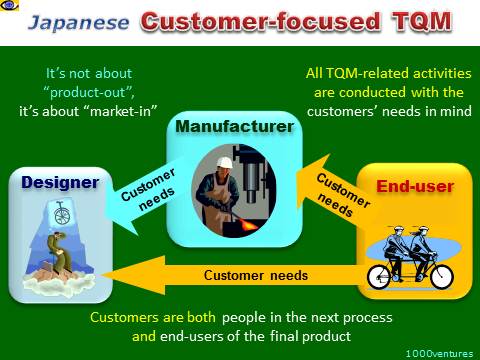
Customer-focused TQM
TQM in Japan is referred to as
“market-in” because it is
customer-focused.
Customer-oriented TQM means that one
should always
satisfy and never inconvenience the people in the next
process because they are customers.
|
|
 |
| |
TQM and Kaizen
Kaizen and TQM is a movement
aimed at continuous improvement
of managerial performance and
quality at all levels.
'Kaizen' means continuous
improvement. One of the most
difficult aspects of introducing
and implementing Kaizen strategy
is assuring its continuity.
When a company introduces
something new, such as quality
circles, or total quality
management (TQM), it experiences
some initial success, but soon
such success disappear like
fireworks on summer night and
after a while nothing is left,
and management keeps looking for
a new flavor of the month.
This is because the company
lacks the first three most
important conditions for the
successful introduction and
implementation of Kaizen
strategy.
|
|
Kaizen
Kaizen
Mindset |
|
| |
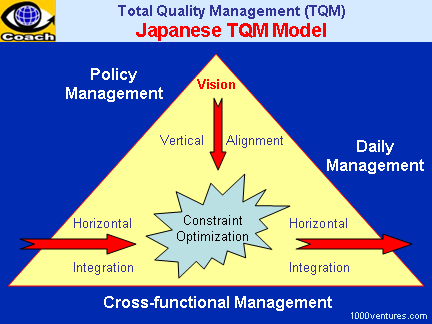
Cross-functional Management
Cross-functional management (CFM)
manages business processes
across the traditional
boundaries of the functional
areas. CFM relates to
coordinating and synergizing the
activities of different units
for realizing the superordinate
cross-functional goals and
policy deployment. It is
concerned with building a better
system for achieving such
cross-functional goals as
innovation, quality, cost, and
delivery.
|
|
Kaizen
Kaizen
Mindset |
|
|
|