| |
Circular
business models are
effective and efficient business models that are closing, narrowing,
slowing, intensifying, and dematerializing loops, to minimize the resource
inputs into and the waste and emission leakage out of the organizational
system.
|
|
 |
|
|
|
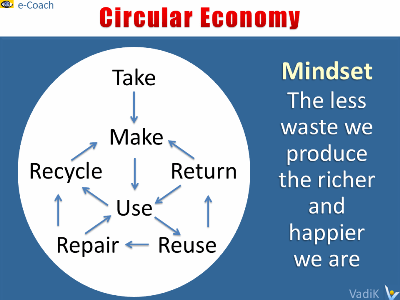
Circular business models integrate
harmonious-growth and
sustainable-business approaches,
ecodesign,
cleaner production,
waste minimization,
recycling measures (closing),
efficiency improvements
(narrowing), use phase extensions (slowing or extending), a more intense use
phase (intensifying), and the substitution of product utility by service and
software solutions (dematerializing).
While the initial focus
of academic, industry,
and policy activities
was mainly focused on
the development of re-X
(reducing, recycling,
remanufacturing, reuse,
recovery)
technology, it soon
became clear that the
technological
capabilities
increasingly exceed
their implementation.
To
leverage technological
capabilities
for the transition
towards a
Circular Economy,
different stakeholders
tend to work together.
They shifts attention
towards
business model
innovation as a key
leverage for 'circular' technology adaption and
harmonious innovation.
|
|
|
|